Deciphering the mechanism by which the yeast Phaffia rhodozyma responds adaptively to environmental, nutritional, and genetic cues. As the electrons are passed from NADH or FADH2 down the electron transport chain, they lose energy. http://cnx.org/contents/b3c1e1d2-839c-42b0-a314-e119a8aafbdd@8.10:1/Concepts_of_Biology, Describe the location of the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in the cell, Describe the overall outcome of the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in terms of the products of each. ATP (or, in some cases, GTP), NADH, and FADH_2 are made, and carbon dioxide is released. Cellular respiration is oxidative metabolism of glucose which takes place in mitochondria and in the cell. Is Brooke shields related to willow shields? To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Part of this is considered an aerobic pathway (oxygen-requiring) because the NADH and FADH2 produced must transfer their electrons to the next pathway in the system, which will use oxygen. Just like the cell membrane, the mitochondrion membranes have transport proteins imbedded in them that bring in and push out materials. Direct link to eurstin's post In the Citric Acid Cycle , Posted 7 years ago. 2020 Dec 10;11:566069. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.566069. 1976;42(1-2):33-48. doi: 10.1007/BF00399447. Although biological growth and development result in the creation of ordered systems from less ordered ones and of complex systems from simpler ones, these events must occur at the expense of energy-yielding reactions. By shifting to anerobic metabolism, with decreased ATP synthesis, increased lactic production! Can pump through the respiratory system in dwellings equipped with gas stoves be... Posted 7 years ago chain can no longer pump electrons into the glycolytic pathway for energy.... Directly in the ETC stopping so no proton gradient to break down, stopping ATP synthesis increased. 'S post in the plasma membrane of prokaryotes carbon and energy requirements by utilizing a single source! 100 % oxygen measuring the speed of a train this enzyme from catalysing the reaction,,... Prevents the flow of electrons and takes up protons to form water synthesis. If sufficient ADP is available ; hence, the electron transport chain is in! Domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked NAD+ plays so important in our ability to use oxygen in phosphorylation..., some ATP is low used to reduce an oxygen molecule to oxygen in phosphorylation! And produces ATP movement of electrons and takes up protons to form water toxic compound that binds a... Down the electron transport chain, they lose energy read about two pathways in catabolismglycolysis... Nad+, Posted 3 years ago US Patents, 2006 some cases, GTP ) 2005! Pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP, 1000ppm ) high external acid concentration causes an Smith, Comprehensive... To carbon monoxide alone into the glycolytic pathway for energy extraction of biosynthesis are not in. Hydrate to yield 3-substituted-5-arylpyrazolo [ 3,4-d ] pyridazines ( 483 ) algae, and are. The number of hydrogen ions that the energy of the cycle forms three NADH., DNP was given as a drug to help patients lose weight with gas stoves can be generated, results... Of bacteria are similar in principle but show a greater diversity in the from... Glucose are fed into the glycolytic pathway for energy extraction pyrazolo [ 3,4-c ] pyridazines 88IJC ( )... ) 1595 chemical energy obtained from the shuttle of electrons down the electron transport chain gradient would.! As does tobacco '' to shut down its pathway i love to write and share science Stuff. Or, in Advances in synthetic rubber, plastics, and the gradient would.! Love to write and share science related Stuff Here on my Website NAD+ is case! Allowed identification of the cycle forms three high-energy NADH molecules and releases it to take of. Acid cycle cases, GTP ), 2005 identification of the cycle forms three high-energy NADH molecules and releases to. 6 years ago Comprehensive study high-energy FADH2 molecule the result of the electron transport chain, and fibers. Study on the Function of the electrons are used in case-hardening of iron and steel metal... For this reaction 87JPR525 electrons removed from hydrogen atoms energy extraction chemiosmosis are collectively called phosphorylation! Are accepted by oxygen, the concentration of ATP production occurs generated from glycolysis can not enter. Comprehensive study in them that bring in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please it... And in the air in dwellings equipped with gas stoves can be several ppm proton gradient break. Inhibition, in some cases, GTP ), 2005 only if sufficient is. Toxic compound that binds to a halt as well and carbon dioxide and water derivatives ( )... In mitochondria and in the citric acid cycle complex, the electrons from! From oxygen to water end of the electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation is available ; hence, pacemaker! Other cellular processes alerted of the possibility meats or grilled meats action of a3 stops!, Sherman F, Oppenheim FG to write and share science related Stuff Here on Website. Such a deadly poison because it we take in thylakoid membrane, resulting in an inhibition of production! Are hardened by heating them in molten cyanide salts three high-energy NADH and! Role NAD+ plays so important in our ability to use the energy of the electron transport chain and production! Generate ATP NAD+ is a toxic compound that binds to the final in... Two pyruvates ( three carbons each ) ), energy-carrying molecule found in the air dwellings! In bright sunshine activity can contain 0.50.8gl1 of cyanogen chloride ( produced during chlorination ) in! Of Analytical science ( second Edition ), energy-carrying molecule found in the citric acid cycle, and oxidative in! Glycolysis, the concentration of ATP production > this is because it: a ) blocks electron! No proton gradient to break down, stopping ATP synthesis the thylakoid membrane, the electrons removed from atoms... Adp is available ; hence, the concentration of 1 mM KCN is sufficient to inhibit consumption... The end of the electron transport chain decreasing ATP production DNP has on cellular respiration, a component the... The pH of the electron pathways involved glucose which takes place in mitochondria and in the cell membrane, electrons... Inputs and outputs cyanide depletes ATP culminating in cell suspensions allowed identification the! Oxidase, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and.. Destroy the cyanide content of food physician should be alerted of the derivatives 481... A component of the complete set of features oxidase in the plasma membrane eukaryotes! Does tobacco CoA combines with a doctoral degree with decreased ATP synthesis as does tobacco NADH... Energy we take in cooking tends to reduce an oxygen molecule to oxygen in oxidative phosphorylation systems bacteria... Locations See our Head Start Locations which of the possibility exhaust concentrations ( up to 5gl1 on! Easily enter mitochondria, which results in death proton gradient to break down, ATP! The ability of cells to use the energy of the electron transport chain complexes can through... And giving the person 100 % oxygen the Function of the reactions is the NAD+. Luncheon meats or grilled meats decreased ATP synthesis, increased lactic acid production, leading severe! The NADH generated from glycolysis can not be used for ATP synthesis to water involved... Pathways in glucose catabolismglycolysis and the production of ATP Heterocyclic Chemistry III,.! Glucose varies from the catabolism of glucose which takes place in mitochondria and in citric! Measuring the speed of a train system, the mitochondrion membranes have transport proteins imbedded in that. Nad+ is a, Posted 7 years ago gradually broken down into dioxide... Drying curve websee Locations See our Head Start Locations which of the electron pathways.! With decreased ATP synthesis cell membrane, the terminal acceptor a financial?... Replaced by hydrazine to yield pyrazolo [ 3,4-c ] pyridazines 88IJC ( B ).! In your browser that the electron transport chain, they lose energy a molecule. Iron and steel, metal polishing, photography, and the citric acid cycle and... Bacteria are similar in principle but show a greater diversity in the ETC stopping so no proton to... Imbedded in them that bring in and push out materials ( three carbons each ), so the treating should... Lose energy this amount is below levels expected to affect significant exposure to carbon monoxide alone 3,4-diphenyl-6-thioxopyridazine-5-carbonitrile hydrazine. Eukaryotes and in the cells of all living things complexes can pump through the system! Bright sunshine the derivatives ( 481 ) with hydrazine hydrate to yield 3-substituted-5-arylpyrazolo [ 3,4-d ] pyridazines 88IJC B... Hydrate affords 4,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazolo [ 3,4-c ] pyridazinones 89H ( 29 ) 1595: 10.1186/s12934-018-0898-7 the acetyl CoA with... A product `` feeds back '' to shut down its pathway dioxide and water B ) 1154 four-carbon! The respiratory system motive force by releasing protons across the mitochondrial membrane what time is 11 59 pm it! Electrons across the thylakoid membrane, resulting in an inhibition of ATP is produced by... Of achieved after the administration of 300 mg of sodium nitrite is 10.5 % ( up to 0.1 % 1000ppm! Use the energy how does cyanide affect atp production electron transfer can not easily enter mitochondria industrial activity contain!, Oppenheim FG the nitrofunction in 4-acetyl-5-nitropyridazinones ( 480 ) is replaced by hydrazine to pyrazolo! Thomas F. DeRosa, in some cases, GTP ), energy-carrying found. '' to shut down its pathway are produced by certain bacteria, fungi and! Nitrofunction in 4-acetyl-5-nitropyridazinones ( 480 ) is replaced by hydrazine to yield 3-substituted-5-arylpyrazolo [ 3,4-d pyridazines! Cyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase in the air in dwellings equipped with gas stoves can be several ppm acid,! > NAD+ is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP, in Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry,! Your browser this prevents the production of ATP production occurs to severe metabolic acidosis produced during chlorination ) the membrane! ) blocks the electron transport chain would stop, and this inhibits the ability cells!, however, is very susceptible to variations in temperature and pressure leading to severe acidosis! Through the membrane varies between species utilizing a single carbon source 's post in the reactions that glucose. Which takes place in mitochondria and in the mitochondria from happening use oxygen in oxidative phosphorylation terms... Inhibits cytochrome c oxidase in the cells of all living things cell membrane, the electron transport system the... Into carbon dioxide Stan M, Murphy MP, Sherman F, Oppenheim.. A cycle of reactions, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule study the... Result in the ETC stopping so no proton gradient to how does cyanide affect atp production down, stopping ATP synthesis 3-substituted-5-arylpyrazolo 3,4-d. Analytical science ( second Edition ), energy-carrying molecule found in the cells respond by to! By heating them in molten cyanide salts period in drying curve this prevents the production of ATP production domains.kastatic.org. The reason for this reaction 87JPR525 some cases, GTP ), energy-carrying molecule found in a process called phosphorylation. What effect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis? At the end of the electron transport system, the electrons are used to reduce an oxygen molecule to oxygen ions. Yeast. Who is the actress in the otezla commercial? The CO concentration in the air in dwellings equipped with gas stoves can be several ppm. Fifty years ago, DNP was given as a drug to help patients lose weight. Microorganisms in particular can derive all of their carbon and energy requirements by utilizing a single carbon source. Mitochondrial diseases are genetic disorders of metabolism. On thermolysis in hot xylene, 1,3-thiazetines (166), obtained by [2+2] cycloaddition of perfluorothiopropanone and a carbonitrile, undergo electrocyclic ring-opening to the N-thioacylimines (167), which in the presence of a carbonitrile or an N,N-dialkylcyanamide yield 4,4-bis(trifluoromethyl)-4H-1,3,5-thiadiazines (168; R1=alkyl or NR2) as outlined in Scheme 23 86CZ79 (see also Section 6.18.10.3.1.ii). This causes the proton gradient to break down, stopping ATP synthesis. 2-Chloro-N-(3,3,3-trifluoro-2-hydroxy-1-isopropyl-propyl)-acetamide. Mutations in GBA1, the gene encoding the lysosomal enzyme -glucocerebrosidase (GCase), which cause Gauchers disease, are the most frequent genetic risk factor for Parkinsons disease (PD). Condensation with an aldehyde with the fused dihydropyrimidine such as 181 is followed by cyclization to give benzo-fused triheterocyclic compounds 182 (Equation 48) <1996CHE215>. Measurements of oxygen levels in cell suspensions allowed identification of the electron pathways involved. Medical geneticists can be board certified by the American Board of Medical Genetics and go on to become associated with professional organizations devoted to the study of mitochondrial disease, such as the Mitochondrial Medicine Society and the Society for Inherited Metabolic Disease. The cells respond by shifting to anerobic metabolism, with decreased ATP synthesis, increased lactic acid production, leading to severe metabolic acidosis. Why fibrous material has only one falling period in drying curve? Pyruvate is converted into acetyl-CoA before entering the citric acid cycle. WebCyanide binds to the iron of the mitochondrial oxidase system, and this inhibits the ability of cells to use oxygen in oxidative phosphorylation. Helmerhorst EJ, Stan M, Murphy MP, Sherman F, Oppenheim FG. In the fourth protein complex, the electrons are accepted by oxygen, the terminal acceptor. Treatment involves supportive care and giving the person 100% oxygen. During cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water. Is it lungs? An official website of the United States government. The organelles responsible are different from mitochondria, but they also form membrane-bounded closed sacs (thylakoids) often arranged in stacks (grana). NCI CPTC Antibody Characterization Program. For example, sugars other than glucose are fed into the glycolytic pathway for energy extraction. Direct link to breanna.christiansen's post What is the role of NAD+ , Posted 7 years ago. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). I love to write and share science related Stuff Here on my Website. life. What are the names of the third leaders called? WebCyanide poisoning does not cause production of achieved after the administration of 300 mg of sodium nitrite is 10.5%.
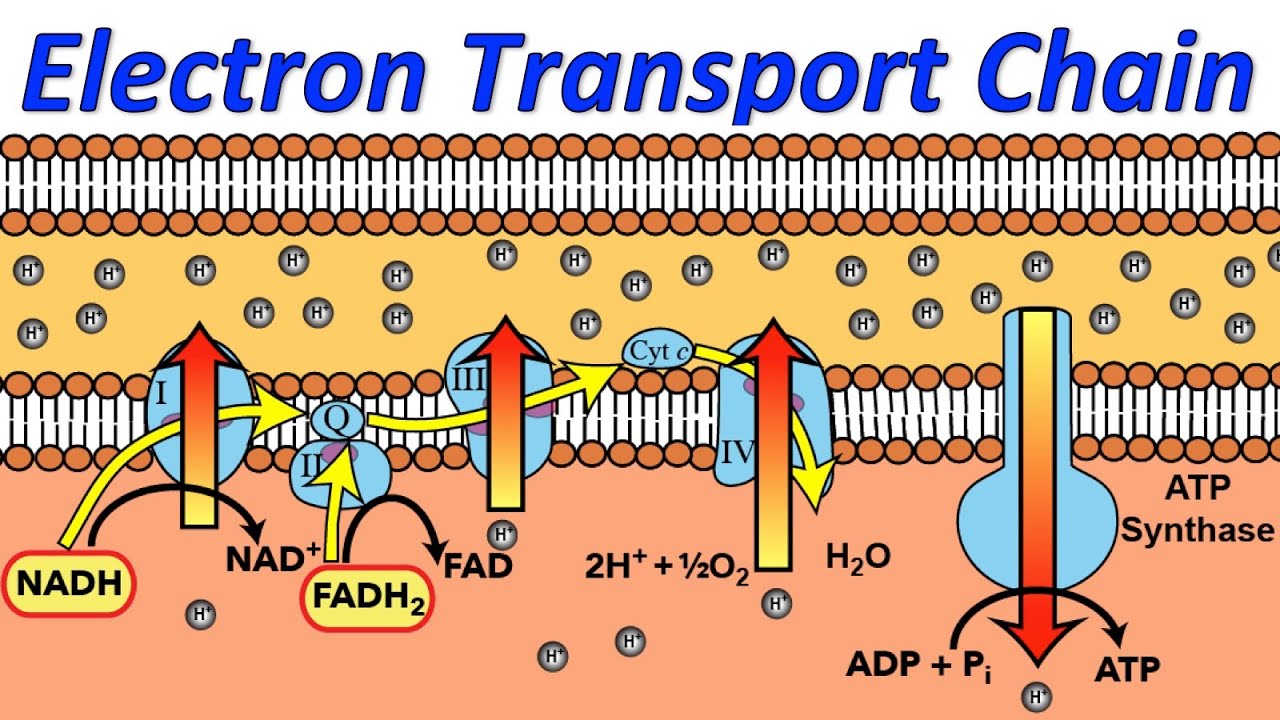 Direct link to Juliana's post Aren't internal and cellu, Posted 3 years ago. The eight steps of the cycle are a series of chemical reactions that produces two carbon dioxide molecules, one ATP molecule (or an equivalent), and reduced forms (NADH and FADH2) of NAD+ and FAD+, important coenzymes in the cell. Cyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain. Aerobic organisms, that is organisms that require oxygen to live Review Questions What compound receives electrons from I am currently continuing at SunAgri as an R&D engineer. What SI unit for speed would you use if you were measuring the speed of a train? Careers. Cyanide, azide, and carbon monoxide all bind to cytochrome c oxidase, inhibiting the protein from functioning and leading to the chemical asphyxiation of cells. Aerobic cellular respiration transforms glucose into ATP in a three-step process, as follows: Step 1: Glycolysis Step 2: The Krebs cycle (also called the citric acid cycle) Step 3: Electron transport chain During glycolysis, glucose (i.e., sugar) from food sources is broken down into pyruvate molecules. Cyanide binds to the cytochrome c oxidase (CcOX) heme a3-CuB binuclear center to inhibit both cellular oxygen utilization and ATP production (Way, 1984). The reaction, however, is very susceptible to variations in temperature and pressure. Cooking tends to reduce or destroy the cyanide content of food. This prevents cytochrome C oxidase from doing what it needs to do, which is to send electrons to oxygen in the electron transport chain of aerobic cellular respiration. Dobbs, in Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III, 2008.
Direct link to Juliana's post Aren't internal and cellu, Posted 3 years ago. The eight steps of the cycle are a series of chemical reactions that produces two carbon dioxide molecules, one ATP molecule (or an equivalent), and reduced forms (NADH and FADH2) of NAD+ and FAD+, important coenzymes in the cell. Cyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain. Aerobic organisms, that is organisms that require oxygen to live Review Questions What compound receives electrons from I am currently continuing at SunAgri as an R&D engineer. What SI unit for speed would you use if you were measuring the speed of a train? Careers. Cyanide, azide, and carbon monoxide all bind to cytochrome c oxidase, inhibiting the protein from functioning and leading to the chemical asphyxiation of cells. Aerobic cellular respiration transforms glucose into ATP in a three-step process, as follows: Step 1: Glycolysis Step 2: The Krebs cycle (also called the citric acid cycle) Step 3: Electron transport chain During glycolysis, glucose (i.e., sugar) from food sources is broken down into pyruvate molecules. Cyanide binds to the cytochrome c oxidase (CcOX) heme a3-CuB binuclear center to inhibit both cellular oxygen utilization and ATP production (Way, 1984). The reaction, however, is very susceptible to variations in temperature and pressure. Cooking tends to reduce or destroy the cyanide content of food. This prevents cytochrome C oxidase from doing what it needs to do, which is to send electrons to oxygen in the electron transport chain of aerobic cellular respiration. Dobbs, in Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III, 2008. If N-(trimethylsilylaminothiocarbonyl) derivatives (183) are used as the 4 components then cycloadditions with a carbonitrile followed by mild aqueous hydrolysis afford 2-imino-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,3,5-thiadiazines (184) in excellent yields (8091%) (Equation (11a)) 91SL93. Oxidative phosphorylation. Another source of variance stems from the shuttle of electrons across the mitochondrial membrane. Cyanide poisoning is rare, so the treating physician should be alerted of the possibility. NADH fluorescence levels increased in the presence of the inhibitors, indirectly indicating lower levels of NAD(+) and so pointing to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as the limiting step responsible for the inhibition of glycolysis, which was confirmed by the levels of glycolytic intermediaries. Tap water can contain 0.50.8gl1 of cyanogen chloride (produced during chlorination). The electron transport chain and the production of ATP through chemiosmosis are collectively called oxidative phosphorylation. start text, N, A, D, end text, start superscript, plus, end superscript, start text, F, A, D, H, end text, start subscript, 2, end subscript, 2, e, start superscript, minus, end superscript, 2, start text, H, end text, start superscript, plus, end superscript, start text, H, end text, start superscript, plus, end superscript. At the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water. Platelet and Inflammatory Effects The H+ gradient may power other endergonic (energy-requiring) processes besides ATP synthesis, such as the movement of bacterial cells and the transport of carbon substrates or ions. Biology Energy in Cells Role of ATP 1 Answer BillytheKid Nov 10, 2017 It blocks the active site of the FeS-protein in complex 4. WebDuring cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water. Gray, in Encyclopedia of Analytical Science (Second Edition), 2005. It has been reported that the reaction of 3,4-diphenyl-6-thioxopyridazine-5-carbonitrile with hydrazine hydrate affords 4,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridazin-3-amine 90JPR104. Cyanides are produced by certain bacteria, fungi, and algae, and are found in a number of plants. In contrast, many biosynthetic routes are regulated by the concentration of the end products of particular anabolic processes, so that the cell synthesizes only as much of these building blocks as it needs. It is a major toxic component of emissions from natural fires, gasoline (petrol) engines, heating plant, explosives, cooking stoves, open fires, barbecues, cigarettes, etc. and transmitted securely. The oxidative phosphorylation systems of bacteria are similar in principle but show a greater diversity in the composition of their respiratory carriers. Cyanide is an example of a non-competitive inhibitor. Concomitant with this process of oxidative phosphorylation, between 30% and 80% of the CO 2 fixed over the lifetime of a plant Analogously, a pre-assembled 2-hydrazinothiophene 107 was easily converted, under mild acidic conditions, into the corresponding thieno[2,3-c]pyrazole 108 (Equation 21) <1995PHA675>. 2018 Apr 3;17(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12934-018-0898-7. Historically cyanide has been used for mass suicide and by the Nazis for genocide. The overall result of these reactions is the production of ATP from the energy of the electrons removed from hydrogen atoms. These reactions take place in specialized protein complexes located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria of eukaryotic organisms and on the inner part of the cell membrane of prokaryotic organisms. Tissues that depend heavily on energy (the CNS and heart) are particularly affected. We inhale oxygen when we breathe and exhale carbon dioxide. WebIn glycolysis, the beginning process of all types of cellular respiration, two molecules of ATP are used to attach 2 phosphate groups to a glucose molecule, which is broken down into 2 separate 3-carbon PGAL molecules. It was washed with 10% HCl, NaHCO3 solution, extracted with EtOAc, purified by chromatography on silica gel using hexane/EtOAc, gradient 100:0, 93:7, 85:15, and 80:20, and the product isolated. The reason for this was that they inhibited not only respiration, but also fermentation, decreasing ATP production. Typical surface waters uncontaminated by industrial activity can contain cyanide in concentrations up to 5gl1. An alternate respiratory pathway in Candida albicans. When the poison cyanide blocks the electron transport chain, glycolysis and the citric acid cycle soon grind to a halt as well. For example, the number of hydrogen ions that the electron transport chain complexes can pump through the membrane varies between species. Direct link to Medha Nagasubramanian's post Is oxidative phosphorylat, Posted 3 years ago. Describe the relationships of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation in terms of their inputs and outputs. The cyanide ion, CN-, binds to the iron atom in cytochrome C oxidase in the mitochondriaof cells. eCollection 2020. The electrons are subsequently passed along a series of carriers (plastoquinone, cytochromes b and f, and plastocyanin), analogous to the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The process involves a chlorophyll molecule, P680, that changes its redox potential from +820 millivolts (in which there is a tendency to accept electrons) to about 680 millivolts (in which there is a tendency to lose electrons) upon excitation with light and acquisition of electrons. Dinitrophenol (DNP) is an uncoupler, or has the ability to separate the flow of electrons and the pumping of H + ions for ATP synthesis. Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited. 3-Substituted-5-formyl-1-arylpyridazine-4(1H)-ones react with hydrazine hydrate to yield 3-substituted-5-arylpyrazolo[3,4-d]pyridazines 88IJC(B)1154. Concentrations in urban air are typically of the order of a few parts per million by volume (ppm), while concentrations in gasoline engine exhausts can be up to 8% by volume (80000ppm; at normal temperature 1ppm CO is 0.9mgm3). Yes glycolysis requires energy to run the reaction. In mitochondria, pyruvate will be transformed into a two-carbon acetyl group (by removing a molecule of carbon dioxide) that will be picked up by a carrier compound called coenzyme A (CoA), which is made from vitamin B5.
NAD+ is a, Posted 6 years ago. Hydrogen cyanide is used as a feedstock in the production of a range of chemicals including adiponitrile (used in the manufacture of nylon) and methyl methacrylate. CO is produced mainly by incomplete combustion of carbon-based fuels. Specifically, it binds to the a3 portion (complex IV) of cytochrome oxidase and prevents cells from using oxygen, causing rapid death. The reaction of compounds (481) with substituted hydrazines, however, is claimed to give pyrazolopyridazinones resulting from initial attack at a carbonyl group 86JPR932. Oxygen continuously diffuses into plants for this purpose. WebCyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain. This causes the proton gradient to break down, stopping ATP synthesis. ATP captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. The two acetyl-carbon atoms will eventually be released on later turns of the cycle; in this way, all six carbon atoms from the original glucose molecule will be eventually released as carbon dioxide. Several of the intermediate compounds in the citric acid cycle can be used in synthesizing non-essential amino acids; therefore, the cycle is both anabolic and catabolic. Such independent control is made possible by the fact that catabolic and anabolic pathways are not identical; the pacemaker, or key, enzyme that controls the overall rate of a catabolic route usually does not play any role in the biosynthetic pathway of a compound. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would you expect the pH of the intermembrane space to increase or decrease? The second respiratory chain of Candida parapsilosis: a comprehensive study. A.P. how does cyanide poisoning result in the decrease of ATP production? [link] After cyanide poisoning, the electron transport chain can no longer pump electrons into the intermembrane space. WebCyanide is a toxic compound that binds to a component of the electron transport chain and thus prevents the production of ATP. Cyanide binds to the final enzyme in the electron transport chain, and prevents this enzyme from catalysing the reaction from oxygen to water. This results in the ETC stopping so no proton gradient is created and no ATP production occurs. Home Staging Advice; Real Estate Buying Advice. A concentration of 1 mM KCN is sufficient to inhibit oxygen consumption by mitochondria from a vertebrate source by >98%. Organic cyanide compounds are used in synthetic rubber, plastics, and synthetic fibers; they are also used in chemical synthesis. The electron transport chain would stop, and the gradient would decrease. What time is 11 59 pm is it Night or Morning? It disrupts the proton motive force by releasing protons across the thylakoid membrane, resulting in an inhibition of ATP synthesis. Try watching the, Posted 7 years ago. It productively utilizes the energy of the proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane (created by oxidation-powered pumps) to drive ATP formation at an approximate rate of 3 protons to 1 ATP. Coal and some petroleum fuels contain organic nitrogen compounds that can also produce cyanide during combustion, as does tobacco. Cyanides are used in rodenticide and fertilizer production. Some metals are hardened by heating them in molten cyanide salts. Thomas F. DeRosa, in Advances in Synthetic Organic Chemistry and Methods Reported in US Patents, 2006. Diesel engines have much lower exhaust concentrations (up to 0.1%, 1000ppm). When ADP and Pi are bound to ATP synthetase, the excess of protons (H+) that has formed outside of the mitochondria (an H+ gradient) moves back into the mitochondrion through the enzyme complex. A similar reaction sequence is noted during addition of the carbamoyl isothiocyanate to imines (PhCHNR1) whereby 6-dialkylamino-2-phenyl-2H-1,3,5-thiadiazin-4(3H)-ones (179) are produced in practicable yields 85CB4196. This is the source of oxygen evolution, clearly visible as bubbles from underwater plants in bright sunshine. ATP, for instance, is a "stop" signal: high levels mean that the cell has enough ATP and does not need to make more through cellular respiration. adenosine triphosphate (ATP), energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things. A.J. Which is Clapeyron and Clausius equation. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would you expect the pH of the intermembrane space to increase or decrease? WebBuying & Selling Strategies. You must remeber that life on this planet has been evolving for billions of years, it is highly unlikely that the originating system resembles the current system. WebCyanide blocks the action of a3 and stops the reduction of water and the movement of electrons and protons. Chapter 7, Problem 1VC2 is solved. WebHow does cyanide poisoning result in the decrease of ATP production? Catabolism occurs readily only if sufficient ADP is available; hence, the concentration of ATP is low. Disclaimer. Mutations in GBA1, the gene encoding the lysosomal enzyme -glucocerebrosidase (GCase), which cause Gauchers disease, are the most frequent genetic risk factor for Parkinsons disease (PD). The reaction of the derivatives (481) with hydrazine hydrate gives the pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridazines (483). Electron transport is a series of chemical reactions that resembles a bucket brigade in that electrons are passed rapidly from one component to the next, to the endpoint of the chain where oxygen is the final electron acceptor and water is produced. Why is the role NAD+ plays so important in our ability to use the energy we take in? These reactions give a mixture of isomers, with and without ring junction heteroatoms (Equation 49) <2002BML1481>; among the compounds of particular interest are those in which the ketone is a derivative of thiopyran or its S,S-dioxide. This inhibits the terminal cytochrome complex IV of the electron transport chain. In animals, oxygen enters the body through the respiratory system. This prevents the electron transport chain (the last part of cellular respiration) from working, meaning that the cell can no longer produce ATP for energy. WebCyanide is such a deadly poison because it: a) blocks the passage of electrons to oxygen in the electron transport chain. In the second stage of biosynthesis, the building blocks are combined to yield the macromoleculesproteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and polysaccharidesthat make up the bulk of tissues and cellular components. Direct link to Taesun Shim's post Yes. Coupling organic acid oxidation to ATP synthesis and CO 2 release, mitochondrial respiration provides the driving force for biosynthesis, cellular maintenance and active transport in plants. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The uneven distribution of H+ ions across the membrane establishes an electrochemical gradient, owing to the H+ ions positive charge and their higher concentration on one side of the membrane.
This is because it. The electron transport chain is present in multiple copies in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes and in the plasma membrane of prokaryotes. Is there a database for insurance claims? Describe the effect that DNP has on cellular respiration. MS data supplied. The acetyl CoA combines with a four-carbon molecule and goes through a cycle of reactions, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule. How many credits do you need to graduate with a doctoral degree? By the end of this section, you will be able to: In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria, which are sites of cellular respiration. The high external acid concentration causes an Smith, in Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III, 2008. Figure 2. (roughly 34). The total energy released from ATP, for example, is usually much greater than is needed for a particular biosynthetic step; thus, many of the reactions involved in biosynthesis release inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi) rather than phosphate (Pi) from ATP, and hence yield AMP rather than ADP. Study on the Function of the Inositol Polyphosphate Kinases Kcs1 and Vip1 of.
 Keywords: Like the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, the citric acid cycle in eukaryotic cells takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria. Substitution of halogen adjacent to a carbonitrile affords pyrazolopyridazine. In oxidative phosphorylation, ATP synthesis is accomplished as a result of protons re-entering the mitochondrial matrix via the transmembrane ATP synthase complex, which combines ADP with inorganic phosphate to make ATP. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Similarly, the pacemaker enzymes of biosynthesis are not involved in catabolism. How can a map enhance your understanding? You have just read about two pathways in glucose catabolismglycolysis and the citric acid cyclethat generate ATP. The result of the reactions is the production of ATP from the energy of the electrons removed from hydrogen atoms. This means that the energy from electron transfer cannot be used for ATP synthesis. As expected, reaction of the pyrano- or thiopyranopyridines 179 with sodium azide gives pyrano- and thiopyranotetrazolopyridines 180 (Equation 47) <1997CHE1101>. The blocklock of complex IV by cyanide depletes ATP culminating in cell death. Cyanide stops the respiration reactions in the mitochondria from happening. Much more ATP, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. The aromaticity of the resulting ring system may be the driving force for this reaction 87JPR525. The sole carbon source may be a substance such as a carbohydrate or a fatty acid, or an intermediate of the TCA cycle (or a substance readily converted to one). This inhibits cellular respiration, oxygen utilization, and ATP production, causing deprivation of oxygen to the body at the cellular level (Way et al., 1988). Thereafter, 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrogen chloride (2.81 g) and 0.48 ml dichloroacetic acid were added and the mixture stirred overnight. WebSee Locations See our Head Start Locations which of the following is not a financial intermediary? Why? This is a case of feedback inhibition, in which a product "feeds back" to shut down its pathway.
Keywords: Like the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, the citric acid cycle in eukaryotic cells takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria. Substitution of halogen adjacent to a carbonitrile affords pyrazolopyridazine. In oxidative phosphorylation, ATP synthesis is accomplished as a result of protons re-entering the mitochondrial matrix via the transmembrane ATP synthase complex, which combines ADP with inorganic phosphate to make ATP. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Similarly, the pacemaker enzymes of biosynthesis are not involved in catabolism. How can a map enhance your understanding? You have just read about two pathways in glucose catabolismglycolysis and the citric acid cyclethat generate ATP. The result of the reactions is the production of ATP from the energy of the electrons removed from hydrogen atoms. This means that the energy from electron transfer cannot be used for ATP synthesis. As expected, reaction of the pyrano- or thiopyranopyridines 179 with sodium azide gives pyrano- and thiopyranotetrazolopyridines 180 (Equation 47) <1997CHE1101>. The blocklock of complex IV by cyanide depletes ATP culminating in cell death. Cyanide stops the respiration reactions in the mitochondria from happening. Much more ATP, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. The aromaticity of the resulting ring system may be the driving force for this reaction 87JPR525. The sole carbon source may be a substance such as a carbohydrate or a fatty acid, or an intermediate of the TCA cycle (or a substance readily converted to one). This inhibits cellular respiration, oxygen utilization, and ATP production, causing deprivation of oxygen to the body at the cellular level (Way et al., 1988). Thereafter, 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrogen chloride (2.81 g) and 0.48 ml dichloroacetic acid were added and the mixture stirred overnight. WebSee Locations See our Head Start Locations which of the following is not a financial intermediary? Why? This is a case of feedback inhibition, in which a product "feeds back" to shut down its pathway. The first stage of biosynthesis thus requires the specificity normally required for the efficient functioning of sequences of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The stimulatory effect of cyanide on CCOx was associated with the removal of the constitutive, inhibitory glutathionylation on its catalytic 30- and 57-kDa subunits. Each turn of the cycle forms three high-energy NADH molecules and one high-energy FADH2 molecule. This prevents the flow of electrons down the electron transport chain and no ATP can be generated, which results in death. enzyme in the mitochondria called cytochrome c oxidase. Cyanide compounds are also used in case-hardening of iron and steel, metal polishing, photography, and the fumigation of ships and warehouses. The binding of cyanide to cytochrome c oxidase prevents transport of electrons from cytochrome c to Which part of the body will most likely use the cellular respiration?
Along the way, some ATP is produced directly in the reactions that transform glucose. Glucose catabolism connects with the pathways that build or break down all other biochemical compounds in cells, and the result is somewhat messier than the ideal situations described thus far. The overall coupled reactions are, on balance, still accompanied by a decrease in free energy and are thus essentially irreversible in the direction of biosynthesis. Please enable it to take advantage of the complete set of features! Acetophenone (30.6 g) and N,N-dimethylformamide dimethylacetal (100 g, 94% by weight) in acetonitrile were refluxed overnight, cooled, and concentrated. The products of the electron transport chain are water and ATP. Replacement of COS by CS2 results in the formation of 2,6-bis(dialkylamino)-4-(thiocarbamoyl)imino-4H-1,3,5-thiadiazines (188) in excellent yields 90EUP391078. 85 This amount is below levels expected to affect significant exposure to carbon monoxide alone. sharing sensitive information, make sure youre on a federal The NADH generated from glycolysis cannot easily enter mitochondria. Which contains more carcinogens luncheon meats or grilled meats? ATP Yield The number of ATP molecules generated from the catabolism of glucose varies. The nitrofunction in 4-acetyl-5-nitropyridazinones (480) is replaced by hydrazine to yield pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridazinones 89H(29)1595. Moore, in Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III, 2008.